Geothermal Technology
Geothermal Plant Types
There are three types of plants used for capturing geothermal energy:
- Dry Steam Plants - direct use of steam from a geothermal reservoir to drive a generator turbine
- Flash Steam Plants - convert high pressure water from the earth's interior to steam for driving generator turbines
- Binary Cycle Power Plants - geothermal hot water is used to heat another liquid to steam, which is used to drive a generator turbine
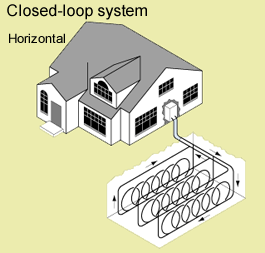
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Temperatures 10 feet below the Earth's surface are consistently between 50 - 60 degrees F. That means that during the winter the Earth can be used to warm buildings, and in the summer it can be used to cool buildings. Heat pumps are used to transfer heat during the winter from the ground into buildings and in the summer transfer heat from buildings into the ground.
Research and Development
The principal impediments to the development of geothermal energy are a set of engineering problems that must be solved in order to make exploration, drilling, extraction and conversion of geothermal energy substantially less risky and more potentially profitable than is currently the case. The basic task is to make the cost of geothermal power competitive with power generated from currently available sources of energy - mostly coal, natural gas, and nuclear energy.
The areas in which research is being conducted are:
- locating and analyzing geothermal resources
- developing drilling techniques necessary for reaching depths of 7 - 10 miles below the surface
- creating fractured rock conditions at those depths where the heat of the rock can be effectively and renewably tapped
- developing a practical Enhanced Geothermal System (EGS) to make geothermal energy more widely available