Coal and the Environment
Introduction
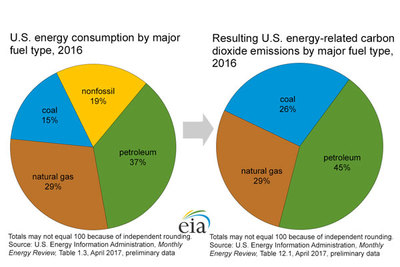
Coal is both an important source of energy for the production of electricity and the most polluting of the fossil fuels. Some of the environmental challenges in the use of coal for generating power are:
- Both mining and burning coal results in the release of greenhouse gases, the principal cause of global warming.
- Its waste products include harmful heavy metals, including some that are radioactive.
- The mining of coal releases acids into ground water and the atmosphere that can cause harm to humans, crops, and wildlife.
- The land at or near mining sites can become unfit for other purposes after mining operations are completed and terminated.
- Mining operations can severely disrupt animal and plant ecosystems, sometimes at extended distances from the mine itself.
Carbon Capture and Sequestration
Of all these issues the one currently receiving the greatest scrutiny is the release of CO2 and other greenhouse gases when coal is burned to produce electricity. One solution to that problem might be carbon capture and sequestration (CCS), in which carbon released at a coal plant is captured in the plant's stack, then compressed and transported to a storage spot, usually an underground void that can hold the CO2 for long periods.